In this tutorial, we’ll delve into the fundamental aspects of MySQL RDBMS, essential for anyone venturing into database management.
We’ll explore the concept of database tables & relational databases, and cover the essentials of MySQL RDBMS with practical examples. First, let’s look at what is a database table.
What is a Database Table?
A database table is a collection of related data organized/structured format into rows and columns, where each row represents a single record, while each column represents a different attribute, data, or field.
Tables are used to store and retrieve data efficiently, making it easy to manage and query large datasets.
Let’s look at this simple user database table, storing information about users registered on a website or application.
| user_id | name | age | created_at | active |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John Smith | 30 | 2023-05-15 | true |
| 2 | Emily Johnson | 25 | 2023-06-20 | false |
| 3 | Michael Williams | 35 | 2023-04-10 | true |
Each row corresponds to a user, and the columns store various attributes of the users, such as
id: A unique identifier for each user.username: The username chosen by each user.age: The age of each user.created_at: The date when each user registered their account.active: A boolean value indicating whether each user’s account is currently active (true) or inactive (false).
With this information, the application could manage user accounts, display user profiles, and perform various operations related to user management.
Your next question will be.
What is a Relational Database?
A relational database organizes data into tables, establishing relationships between them based on shared information, following a structured relational model.
Let’s look at the following example between users, posts, and comments tables.
| user_id | name | age | created_at | active |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John Smith | 30 | 2023-05-15 | true |
| 2 | Emily Johnson | 25 | 2023-06-20 | false |
| 3 | Michael Williams | 35 | 2023-04-10 | true |
| post_id | user_id | title | content | created_at |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | Introduction | Hello everyone! | 2023-05-16 08:00:00 |
| 2 | 2 | Update | New features coming soon! | 2023-06-22 10:30:00 |
| 3 | 1 | Thank you | Thanks for all the support! | 2023-05-18 15:45:00 |
| 4 | 3 | Project Update | Progress update on our project. | 2023-04-12 11:20:00 |
| comment_id | post_id | user_id | comment | created_at |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | 1 | 2 | Great introduction! | 2023-05-16 08:30:00 |
| 102 | 2 | 2 | Looking forward to it! | 2023-06-22 11:00:00 |
| 103 | 1 | 1 | Thanks for sharing! | 2023-05-18 16:00:00 |
You can see highlighted relationships between users, posts, and comments with user_id, post_id, and comment_id columns respectively.
Now, What is RDBMS?
RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System, it is a program used to maintain a relational database.
It’s a type of database management system that organizes data into tables and is structured in a way that establishes relationships between different tables, typically through primary and foreign keys.
The relational aspect refers to the ability to define relationships between data entities, enabling powerful querying capabilities and ensuring data integrity through constraints and rules.
Popular examples of RDBMS include MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle Database, SQL Server, and SQLite. These systems are widely used in various applications ranging from web development to enterprise software solutions due to their flexibility, scalability, and robustness.
RDBMSs use SQL queries to access the data in the database, a topic we’ll cover in the next chapter.
MySQL Sample Database
The following database diagram illustrates the blog database:
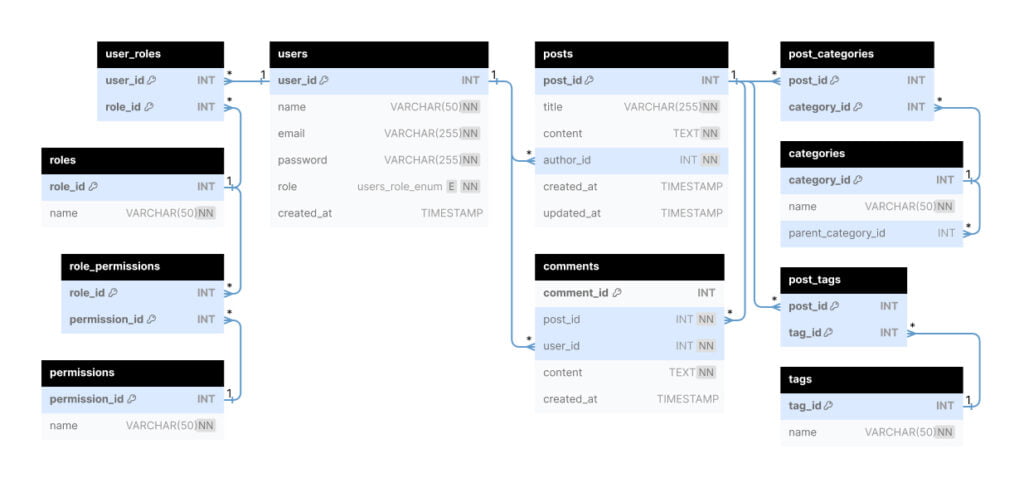
In this schema:
- The
userstable to manage user accounts, including their username, password, email, role, and creation time. - The
poststable stores information about each blog post, including its title, content, author, creation time, and update time. - The
commentstable stores comments made on blog posts, including the comment content, the post it belongs to, the author of the comment, and the creation time. - The
categoriestable holds the categories into which blog posts can be classified. - The
post_categoriestable is a many-to-many relationship between posts and categories, allowing a post to belong to multiple categories. - The
tagstable to store tags that can be associated with blog posts. - The
post_tagstable as a many-to-many relationship between posts and tags. - The
rolestable stores different roles that users can have, such as ‘admin’, ‘author’, or ‘subscriber’. - The
permissionstable holds different permissions that can be assigned to roles. - The
role_permissionstable establishes a many-to-many relationship between roles and permissions. - The
user_rolestable establishes a many-to-many relationship between users and roles, allowing users to have multiple roles.
The following SQL script creates the Blog sample database in MySQL:
Load Data into the MySQL database
Summary
In this tutorial, we’ve explored the fundamental aspects of MySQL RDBMS
- Understanding database tables: Rows represent individual records, while columns store attributes or fields.
- Exploring relational databases: Tables establish relationships based on shared information, following a structured relational model.
- Introducing RDBMS: Software used to maintain relational databases, ensuring data integrity and enabling powerful querying capabilities.
By grasping these concepts, you’re equipped to navigate the world of database management efficiently.
Further exploration into SQL queries will deepen your understanding of database operations and interactions.